Study 215
STUDY DESIGN
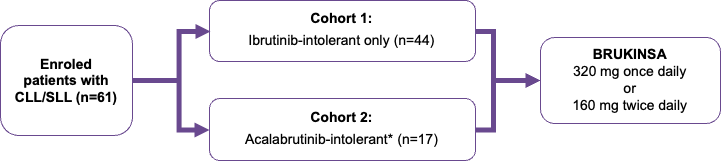
Study 215 was a phase 2, multicentre, open-label, single-arm trial of BRUKINSA in patients with previously treated B-cell lymphoma* who have shown intolerance to prior Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors (Figure 1).1,2
*Study 215 enroled patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia, mantle cell lymphoma, and marginal zone lymphoma.2
Figure 1. Study 215: Study design1,2
Patients
As of January 3, 2023, 61 patients with CLL/SLL were enroled and received ≥1 dose of BRUKINSA.1 Patients were eligible for the Study 215 if they had received ≥4 weeks of ibrutinib and/or acalabrutinib therapy.1
Stratification
Patients were stratified according to BTK inhibitor intolerance; Cohort 1 included patients intolerant to ibrutinib only, and Cohort 2 included patients intolerant to acalabrutinib alone, or acalabrutinib and ibrutinib.1,2
Key baseline characteristics
The key baseline characteristics for Cohorts 1 and 2 are summarised in Table 1.1
Table 1. Study 215: Key baseline characteristics for Cohorts 1 and 21
| Characteristic | Cohort 1: Ibrutinib intolerant (n=44) | Cohort 2: Acalabrutinib intolerant* (n=17) | Total (n=61) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indication, n (%) | |||
| CLL | 38 (86.4) | 15 (88.2) | 53 (86.9) |
| SLL | 6 (13.6) | 2 (11.8) | 8 (13.1) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 23 (52.3) | 9 (52.9) | 32 (52.5) |
| Age, median (range), years | 71.5 (49-91) | 71 (51-83) | 71 (49-91) |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | |||
| 0 | 26 (59.1) | 11 (64.7) | 37 (60.7) |
| 1 | 18 (40.9) | 4 (23.5) | 22 (36.1) |
| 2 | 0 | 2 (11.8) | 2 (3.3) |
| No. of prior anticancer regimens, median (range) | 1 (1-7) | 2 (1-6) | 1 (1-7) |
| Duration of prior ibrutinib therapy, median (range), months | 12.9 (1.2-64.8) | 6.2 (3.1-46.4) | 9.5 (1.2-64.8) |
| Duration of prior acalabrutinib therapy, median (range), months | NA | 5.1 (1.2-33.7) | 5.1 (1.2-33.7) |
| del(17p) mutation, n (%)† | |||
| Present | 4 (9.1) | 2 (11.8) | 6 (9.8) |
| Absent | 32 (72.7) | 8 (47.1) | 40 (65.6) |
| Unmutated IGHV, n (%)† | |||
| Present | 10 (22.7) | 1 (5.9) | 11 (18.0) |
| Absent | 8 (18.2) | 3 (17.6) | 11 (18.0) |
| TP53 mutation, n (%)† | |||
| Present | 11 (25.0) | 3 (17.6) | 14 (23.0) |
| Absent | 27 (61.4) | 6 (35.3) | 33 (54.1) |
Primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was the recurrence and change in severity of intolerance events, based on investigator-assessed adverse events.1,2
Cohort 1
At a median follow-up of 28.2 months, over 90% of ibrutinib intolerance events (87/95 events) did not recur or improved with BRUKINSA, and none recurred at a higher grade (Figure 2).1
Figure 2. Ibrutinib-intolerance events in Cohort 1 (n=44. 95 events; investigator-assessed)1,2
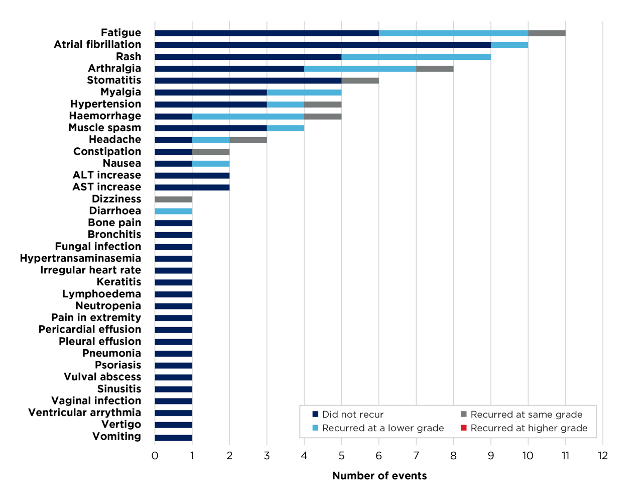
Fewer than 10% (n=4) of ibrutinib-intolerant patients discontinued BRUKINSA due to treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs).1
Cohort 2
At a median follow-up of 10.1 months, over 80% of acalabrutinib intolerance events (17/21 events) did not recur or improved with BRUKINSA, and none recurred at a higher grade (Figure 3).1
Figure 3. Acalabrutinib-intolerance events (n=17. 21 events; investigator-assessed)*1,2
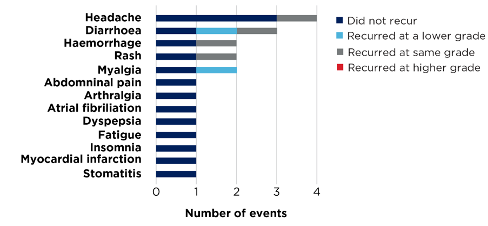
*Includes patients intolerant to acalabrutinib alone, or acalabrutinib and ibrutinib.1,2
Fewer than 6% (n=1) of acalabrutinib-intolerant patients discontinued BRUKINSA due to TEAEs.1
Secondary endpoints
Secondary endpoints in Study 215 were investigator-assessed overall response rate, duration of response, disease control rate, progression-free survival, and health-related quality of life.1,2
In 57 evaluable patients receiving BRUKINSA, 95% (n=54) maintained or improved their response rate.1
